Hi Sereyians, how you doing?. Quite some moments now, seems everything is rocking well based on the community interactions.
Without much ado would like to take you through LUTING and CEMENTATION in the restorative branch of dentistry and their importance with relevant uses.
First of, let's with the definition of each terms relating to the aforementioned concept of luting.
1- Luting
2- Cement
3- Luting agent
Now, let's define the term luting.
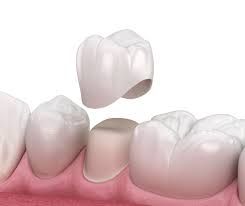
LUTING means joining or cement two or more individual piece of an object, devices, dentures, broken tooth and so on together as one integral piece
In a nutshell, it means joining or integrating something together
A cement in restorative dentistry means any substance or material that hardened to act as liner, base, filling (restorative) material or adhesive(bonding or luting) to bind or integrate devices and prosthesis to tooth structure and to each other as a single entity.
Luting agent any material or substance used to attach, cement or bind indirect restorations such as crowns, bridges, inlays, inlays and so on to a prepared tooth.
It usually serves as an intermediate material between the tooth surface and the restorative materials.
At this point let's get to know about the classification of Luting material specifically in fixed prosthodontics aspect of dentistry.
Luting agents or materials are classified into two which are according to the length of time they are required to stay in function with efficiency and stability. This class are of two types which are :
A - Definitive
B - Interim or Provisional or temporary
The other classification is according to the setting mechanism or the predominant setting mechanism of constituents materials that made up the cement which are could be either acid-base reaction or polymerization reaction.
Now after discussing about the classification in brief let's explore the different types under each classification with vivid explanation.
1- According to the length of time they are expected to function
A- Definitive cements are cement that are used for long term purposes and functions on attachment of dental prostheses and as such they must have sufficient properties that could aid them to arrive at such requirements
They are either water base or polymer
B- Provisional Cements on the other hand are cements that are indicated for attaching temporary restorations which are used in between clinical appointments required to conclude or finish the definitive restorations.
Due to the facts provisional restorations are often needed to be removed in between clinical treatment so they must have a relatively low strength and easily handled with no difficulty for easy disengagement and removal.
Also they should not irritate the pulp and be as biocompatible as possible for good clinical results.
Examples of such cements include : Zinc oxide eugenol, calcium hydroxide among others.
The other classification is the base on their setting reaction or dominant form of their setting which includes the following:
1- Acid Base Reaction
Most of the cements that set with this reaction have a carboxylic acid or simply carboxylate groups or other acidic groups in their chemical structure and as such set with this chemical reaction after mixing them in the clinic or laboratory.
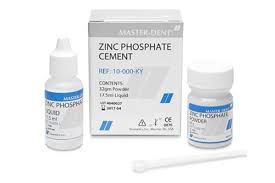
Their examples include the following cements such as; glass ionomer cement (GIC), resin modified glass ionomer cement (RMGIC) or sometimes called resin reinforced glass ionomer cements (RRGIC), zinc oxide eugenol cement, zinc polycarboxylate, zinc phosphate and so on.
2- Polymerization Reaction
Some cements engage in polymerization reaction as their form of setting after their mixing or their working period which means forming and combining together to form a chain of polymer from their constituent monomers by series of additions.
Examples of such types include; compomers, resin cements, self-adhesive resin cements, composite resin materials and so on.
There are some properties that Idea cements need to have as their expected qualities but since there is nothing in dentistry as ideal cement atleast for now. There is nothing wrong in knowing some of those properties which are as follows:
1- A good cement should have sufficient and adequate strength properties of holding the prosthesis and other components together effectively.
2- A good dental cement should possess good working and setting time
3- It should be easily compressible to thin layers
4 - Also, should be easily manipulated
5- It should have low viscosity and solubility
6- It should provide good tight seal and be bacteriostatic in function.
7 - Be biocompatible enough as possible and should be non-irritant to pulp and other dental tissues
8- Adhere well and firmly to both tooth structure and restorative materials
9- It have some optical properties such as in the case of translucent restorations like porcelain and other ceramics
10- Insoluble and non-reacting to saliva and other liquids taken into the mouth
These are the major ideal properties that a dental cement should possess before it could be of effective function and widely acceptable for dental use.
In conclusion let's take a glimpse of some common dental cements which are as follows:
1- Zinc phosphate cements
2- Zinc polycarboxylate cement
3- Glass ionomer cements
4- Resin luting cements
5- Zinc oxide eugenol and its modified form
6- Resin modified glass ionomer cement
7 - Compomers
8 - Composite resin cements among others.
We are going to stop at this juncture atleast for now and then we would continue with discussing on each cements in the subsequent posts.
Thanks for going this length write-up and happy Sereying
Happy Sereying 🌴🌴🌴🌴🌴
Cross-Posted from my Blurt Account


Comments